As the world intensifies its efforts to combat climate change, innovative solutions are emerging to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability. One such approach combines tree planting initiatives with the use of treated wastewater, creating a dual-impact strategy that not only enhances carbon sequestration but also optimizes water resources. This method has the potential to generate carbon credits, offering financial incentives for organizations and communities to adopt eco-friendly practices. However, navigating the complexities of carbon credit certification and implementation can be challenging. This article explores how to effectively integrate tree planting and treated wastewater use into carbon credit projects, providing actionable insights for stakeholders aiming to make a measurable environmental impact.

- Need Help Turning Tree Planting and Treated Wastewater Use into Carbon Credits
- Can I get carbon credits for planting trees?
- How much money do you get per acre for carbon credits?
- How to get carbon credits from trees?
- How to get paid for forest carbon credits?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the process for turning tree planting into carbon credits?
- How does treated wastewater use contribute to carbon credit generation?
- What are the benefits of combining tree planting with treated wastewater use for carbon credits?
- What challenges might arise when turning tree planting and treated wastewater use into carbon credits?
Need Help Turning Tree Planting and Treated Wastewater Use into Carbon Credits
Understanding the Basics of Carbon Credits
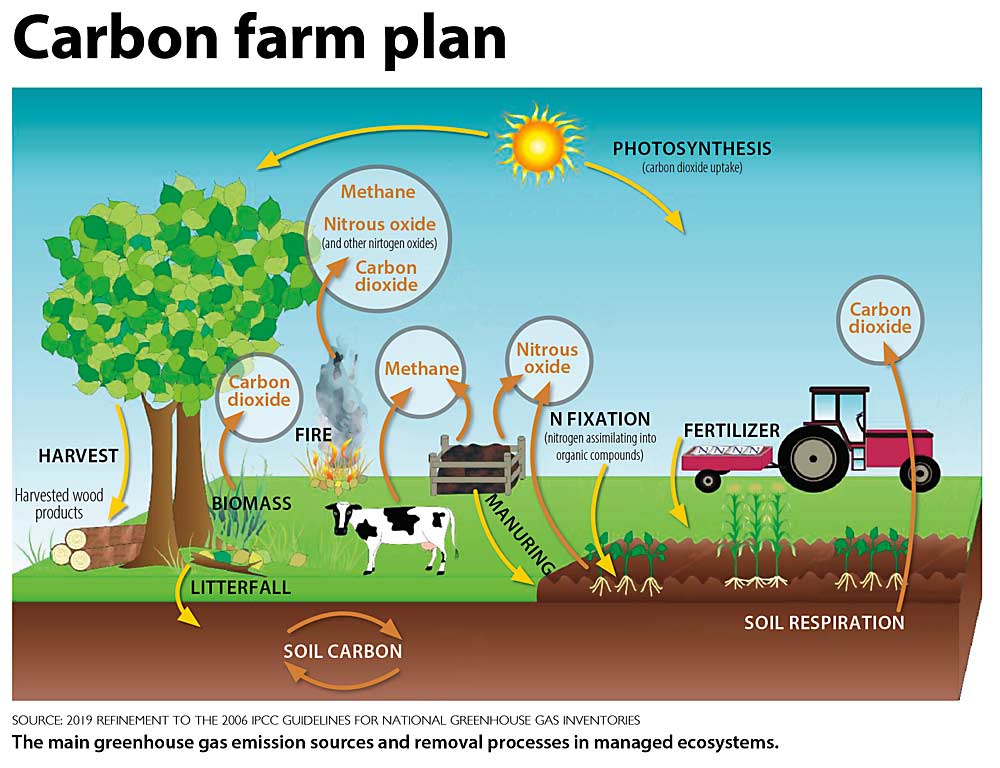
Carbon credits are a form of tradeable certificate that represents the right to emit one ton of carbon dioxide or an equivalent amount of other greenhouse gases. They are a key component in efforts to reduce global carbon emissions. By engaging in activities like tree planting and treated wastewater use, organizations can generate carbon credits, which can then be sold to other entities looking to offset their emissions.
The Role of Tree Planting in Carbon Sequestration
Tree planting is one of the most effective natural methods for carbon sequestration. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis and store it in their biomass. This process not only helps in reducing the overall carbon footprint but also contributes to biodiversity and ecosystem restoration. To turn tree planting into carbon credits, it is essential to measure the amount of carbon sequestered accurately and ensure the project meets specific verification standards.
See Also Tech Giants Join Forces for Carbon Credits: Behind the Hype
Tech Giants Join Forces for Carbon Credits: Behind the HypeUtilizing Treated Wastewater for Environmental Benefits
Treated wastewater can be repurposed for irrigation, industrial processes, and even replenishing natural water bodies. By using treated wastewater, we can reduce the demand for freshwater resources and lower the energy consumption associated with water treatment processes. This reduction in energy use translates to fewer greenhouse gas emissions, making it a viable project for generating carbon credits. Proper documentation and adherence to environmental regulations are crucial for this process.
Steps to Convert Tree Planting and Treated Wastewater Use into Carbon Credits
To successfully convert these activities into carbon credits, follow these steps:
1. Project Development: Design a project that aligns with carbon credit standards.
2. Baseline Assessment: Measure the current carbon emissions or sequestration levels.
3. Implementation: Execute the tree planting or wastewater treatment project.
4. Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously track the project's impact and report findings.
5. Verification and Certification: Have the project verified by a third-party auditor to ensure compliance with carbon credit standards.
Challenges and Solutions in Generating Carbon Credits
Generating carbon credits from tree planting and treated wastewater use comes with its own set of challenges. These include high initial costs, complex verification processes, and long-term maintenance requirements. However, solutions such as securing funding through grants, partnering with experienced organizations, and leveraging technology for accurate monitoring can help overcome these obstacles.
See Also Forests, Finance, and Lessons for the Global Community
Forests, Finance, and Lessons for the Global Community| Activity | Carbon Credit Potential | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Tree Planting | High | Accurate measurement, long-term maintenance |
| Treated Wastewater Use | Moderate | Energy savings, regulatory compliance |
Can I get carbon credits for planting trees?
What Are Carbon Credits?
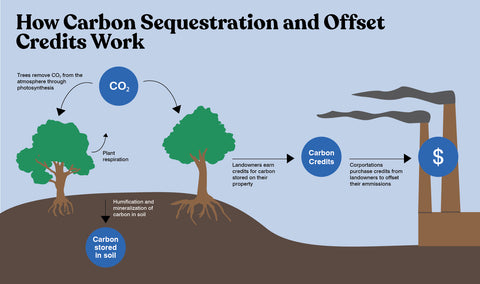
Carbon credits are a form of environmental currency that represent the reduction, avoidance, or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO₂) or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases. These credits are often traded in carbon markets to help organizations offset their emissions. Planting trees can generate carbon credits because trees absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, effectively reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the air.
- Carbon credits are used to offset emissions.
- One credit equals one metric ton of CO₂ removed or avoided.
- Tree planting is a common method to earn carbon credits.
How Does Planting Trees Generate Carbon Credits?
Planting trees can generate carbon credits because trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass. The amount of carbon sequestered depends on factors like tree species, growth rate, and forest management practices. To earn carbon credits, the project must be verified by a recognized carbon standard, such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or the Gold Standard.
See Also Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin?
Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin?- Trees absorb CO₂ and store it in their biomass.
- Carbon sequestration depends on tree species and growth conditions.
- Projects must meet strict verification standards to earn credits.
What Are the Requirements for Earning Carbon Credits from Tree Planting?
To earn carbon credits from tree planting, the project must meet specific criteria set by carbon certification programs. These include demonstrating additionality (proving the project wouldn’t have happened without carbon funding), ensuring permanence (the carbon must remain stored for a long time), and avoiding leakage (ensuring emissions aren’t simply shifted elsewhere).
- Projects must prove additionality to qualify.
- Carbon storage must be permanent and verifiable.
- Leakage must be minimized to ensure environmental integrity.
Which Organizations Certify Carbon Credits from Tree Planting?
Several organizations certify carbon credits from tree planting projects, including the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), the Gold Standard, and the Climate, Community & Biodiversity Standards (CCB). These organizations ensure that projects meet rigorous environmental and social criteria, providing credibility to the carbon credits generated.
- Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) is a leading certification body.
- The Gold Standard emphasizes sustainable development benefits.
- CCB Standards focus on community and biodiversity impacts.
What Are the Challenges of Earning Carbon Credits from Tree Planting?
While planting trees can generate carbon credits, there are challenges, such as ensuring long-term carbon storage, preventing deforestation, and accurately measuring carbon sequestration. Additionally, the costs of project development, monitoring, and verification can be high, making it difficult for small-scale projects to participate.
- Ensuring long-term carbon storage is a major challenge.
- Accurate measurement of carbon sequestration is complex.
- High costs can limit participation for small-scale projects.
How much money do you get per acre for carbon credits?

What Factors Influence the Value of Carbon Credits per Acre?
The amount of money you can earn per acre for carbon credits depends on several factors:
- Type of Land: Forested land typically generates more carbon credits than agricultural or grassland due to higher carbon sequestration rates.
- Geographic Location: Carbon credit prices vary by region due to differences in market demand and regulatory frameworks.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential: The ability of the land to absorb and store carbon dioxide plays a significant role in determining credit value.
- Market Conditions: The current price of carbon credits in voluntary or compliance markets can fluctuate based on supply and demand.
- Project Duration: Longer-term projects often yield higher returns as they provide sustained carbon sequestration.
How Are Carbon Credits Calculated per Acre?
Calculating carbon credits per acre involves several steps:
- Baseline Assessment: Determine the current carbon stock of the land before implementing any carbon sequestration practices.
- Carbon Sequestration Rate: Estimate how much carbon the land can absorb annually based on vegetation type, soil quality, and management practices.
- Verification: Use standardized methodologies and third-party verification to ensure accurate carbon credit calculations.
- Market Pricing: Multiply the verified carbon credits by the current market price to determine the monetary value per acre.
What Is the Average Earnings per Acre for Carbon Credits?
Earnings per acre for carbon credits can vary widely:
- Forest Land: On average, forested land can generate $10 to $50 per acre annually, depending on the factors mentioned earlier.
- Agricultural Land: Carbon credits from agricultural practices like no-till farming or cover cropping may yield $5 to $20 per acre annually.
- Grassland: Grasslands typically earn less, around $2 to $10 per acre annually, due to lower carbon sequestration rates.
How Do Carbon Credit Programs Work for Landowners?
Landowners can participate in carbon credit programs through the following steps:
- Enrollment: Register your land with a carbon credit program or marketplace that aligns with your goals.
- Implementation: Adopt practices that enhance carbon sequestration, such as reforestation or sustainable farming techniques.
- Monitoring: Regularly measure and report carbon sequestration data to ensure compliance with program requirements.
- Credit Issuance: Receive carbon credits based on verified sequestration data, which can then be sold in the market.
What Are the Challenges of Earning Carbon Credits per Acre?
Earning carbon credits per acre comes with certain challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Implementing carbon sequestration practices often requires significant upfront investment.
- Complex Verification: The process of verifying carbon credits can be time-consuming and costly.
- Market Volatility: Carbon credit prices can fluctuate, affecting the predictability of earnings.
- Long-Term Commitment: Many programs require long-term land management commitments, which may not suit all landowners.
How to get carbon credits from trees?

Understanding Carbon Credits and Trees
Carbon credits are a form of environmental currency that represent the reduction or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere. Trees play a crucial role in this process because they absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis and store it as carbon in their biomass. To obtain carbon credits from trees, the following steps are essential:
- Identify a suitable forest or land where trees can be planted or existing forests can be preserved.
- Measure the carbon sequestration potential of the trees using scientific methods and tools.
- Register the project with a recognized carbon credit certification body, such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or the Gold Standard.
Steps to Develop a Carbon Credit Project
Developing a carbon credit project involves a structured approach to ensure the project meets regulatory and environmental standards. Here’s how to proceed:
- Conduct a feasibility study to assess the land, tree species, and potential carbon sequestration.
- Design the project by creating a detailed plan that includes tree planting, maintenance, and monitoring.
- Submit the project for validation by an independent third-party auditor to ensure compliance with carbon credit standards.
Monitoring and Verification of Carbon Sequestration
Accurate monitoring and verification are critical to ensure the carbon credits generated are legitimate. This process involves:
- Regularly measuring tree growth and carbon storage using remote sensing, field surveys, or drones.
- Documenting data to track changes in carbon stocks over time.
- Undergoing periodic audits by certification bodies to verify the carbon credits.
Selling Carbon Credits on the Market
Once carbon credits are verified, they can be sold to individuals, companies, or governments looking to offset their carbon emissions. The steps include:
- Listing the credits on a carbon credit marketplace or platform.
- Negotiating prices based on market demand and the quality of the credits.
- Transferring ownership of the credits to the buyer upon agreement.
Ensuring Long-Term Sustainability
To maintain the integrity of carbon credits, it is essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of the project. This involves:
- Protecting the forest from deforestation, wildfires, and illegal logging.
- Engaging local communities to support conservation efforts and provide economic benefits.
- Adapting management practices to address climate change impacts and ensure continuous carbon sequestration.
How to get paid for forest carbon credits?
Understanding Forest Carbon Credits
Forest carbon credits are a form of environmental commodity that represents the reduction or removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These credits are generated through sustainable forest management practices, such as reforestation, afforestation, and avoided deforestation. To get paid for forest carbon credits, you need to follow a structured process:
- Assess your forest: Determine the carbon sequestration potential of your forest by conducting a carbon inventory.
- Choose a carbon standard: Select a recognized carbon standard like Verra or Gold Standard to certify your project.
- Develop a project plan: Create a detailed plan outlining your forest management practices and how they will reduce or remove carbon emissions.
Registering Your Carbon Project
Once you have a project plan, the next step is to register your carbon project with a recognized carbon registry. This involves submitting your project documentation for review and approval. The registry will verify that your project meets the required standards and issue carbon credits accordingly. Key steps include:
- Submit documentation: Provide all necessary documents, including your project plan, carbon inventory, and monitoring protocols.
- Undergo validation: An independent third party will validate your project to ensure it meets the carbon standard's criteria.
- Register the project: Once validated, your project will be officially registered, and carbon credits will be issued.
Monitoring and Reporting
After your project is registered, ongoing monitoring and reporting are essential to ensure the continued generation of carbon credits. This involves regular data collection and submission to the carbon registry. The process includes:
- Collect data: Regularly measure and record carbon sequestration or emission reductions.
- Submit reports: Provide periodic reports to the carbon registry, detailing your project's performance.
- Undergo verification: An independent verifier will review your reports to confirm the accuracy of your data.
Selling Carbon Credits
Once your carbon credits are issued, you can sell them on the carbon market. There are two main types of markets: compliance markets and voluntary markets. To sell your credits, follow these steps:
- Choose a market: Decide whether to sell your credits in the compliance or voluntary market based on your project's goals and buyer preferences.
- Find buyers: Use carbon market platforms, brokers, or direct negotiations to find buyers for your credits.
- Complete the transaction: Once a buyer is found, complete the sale and transfer the credits to the buyer's account.
Maximizing Revenue from Carbon Credits
To maximize revenue from forest carbon credits, it's important to optimize your project's performance and market strategy. Consider the following tips:
- Enhance carbon sequestration: Implement best practices in forest management to increase the amount of carbon sequestered.
- Diversify buyers: Engage with multiple buyers to ensure competitive pricing and reduce dependency on a single buyer.
- Stay updated: Keep abreast of market trends and regulatory changes to make informed decisions about selling your credits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the process for turning tree planting into carbon credits?
Tree planting can be transformed into carbon credits by following a structured process. First, the project must be designed to meet specific criteria, such as ensuring the trees are planted in a way that maximizes carbon sequestration. This involves selecting appropriate tree species, determining the planting location, and calculating the expected carbon capture over time. The project must then be validated and verified by a recognized carbon standard, such as Verra or the Gold Standard. Once approved, the carbon credits can be issued and sold on the carbon market, providing financial incentives for the project developers.
How does treated wastewater use contribute to carbon credit generation?
Using treated wastewater for irrigation or other purposes can contribute to carbon credit generation by reducing the need for freshwater extraction and treatment, which are energy-intensive processes. Additionally, treated wastewater can enhance soil health and promote plant growth, further increasing carbon sequestration. To generate carbon credits, the project must demonstrate measurable reductions in greenhouse gas emissions or increases in carbon storage. This requires detailed monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) processes to ensure the project meets the standards set by carbon credit certification bodies.
What are the benefits of combining tree planting with treated wastewater use for carbon credits?
Combining tree planting with treated wastewater use offers multiple benefits for carbon credit projects. Firstly, it maximizes the environmental impact by addressing both carbon sequestration and water resource management. Trees irrigated with treated wastewater can grow faster and healthier, leading to higher carbon capture rates. Secondly, this integrated approach can improve the overall sustainability of the project, making it more attractive to investors and stakeholders. Finally, it can create additional co-benefits, such as improved soil quality, enhanced biodiversity, and reduced pressure on freshwater resources, which can further enhance the project's eligibility for carbon credits.
What challenges might arise when turning tree planting and treated wastewater use into carbon credits?
Several challenges can arise when attempting to turn tree planting and treated wastewater use into carbon credits. One major challenge is the complexity of the carbon credit certification process, which requires rigorous documentation, monitoring, and verification. Additionally, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the project can be difficult, as it requires ongoing maintenance and management of both the trees and the wastewater treatment systems. There may also be regulatory hurdles, as different regions have varying rules and standards for carbon credit projects. Finally, securing funding and investment can be challenging, especially for smaller projects that may not have the resources to navigate the complex carbon market.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles