In recent years, the tech industry has faced increasing scrutiny over its environmental impact, prompting major players to explore innovative solutions. One such initiative gaining traction is the collaboration among tech giants to invest in and trade carbon credits. These credits, designed to offset greenhouse gas emissions, have become a focal point in corporate sustainability strategies. However, behind the optimistic headlines lies a complex landscape of challenges and controversies. This article delves into the motivations driving these partnerships, the potential benefits for the environment, and the criticisms surrounding the effectiveness and transparency of carbon credit systems in the tech sector.

Tech Giants Join Forces for Carbon Credits: Behind the Hype
The collaboration of tech giants in the pursuit of carbon credits has sparked significant interest and debate. While the initiative is often portrayed as a groundbreaking step toward sustainability, it is essential to delve deeper into the motivations, challenges, and implications of this partnership. This article explores the behind-the-scenes dynamics of this alliance, shedding light on its potential impact on the environment, the economy, and the tech industry.
What Are Carbon Credits and Why Do They Matter?
Carbon credits are permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit typically equals one ton of CO2. These credits are part of a cap-and-trade system, designed to reduce overall emissions by incentivizing companies to lower their carbon footprint. For tech giants, purchasing carbon credits is a way to offset their environmental impact while maintaining operations. However, critics argue that this system can sometimes serve as a band-aid solution, allowing companies to continue polluting while appearing environmentally responsible.
See Also Forests, Finance, and Lessons for the Global Community
Forests, Finance, and Lessons for the Global CommunityThe Role of Tech Giants in the Carbon Credit Market
Tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have been at the forefront of adopting carbon credit programs. These companies have pledged to achieve carbon neutrality or even carbon negativity in the coming years. By joining forces, they aim to create a more transparent and efficient carbon credit market. Their involvement brings financial resources, technological expertise, and global influence to the table, potentially accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy. However, their dominance in this space also raises concerns about market monopolization and the exclusion of smaller players.
Challenges in Implementing Carbon Credit Programs
Despite the enthusiasm surrounding carbon credits, several challenges persist. One major issue is the lack of standardization in how carbon credits are measured and verified. This can lead to greenwashing, where companies overstate their environmental efforts. Additionally, the high cost of acquiring carbon credits can be a barrier for smaller businesses, creating an uneven playing field. Tech giants must address these challenges to ensure the credibility and effectiveness of their initiatives.
The Environmental Impact of Tech Giants' Carbon Credit Initiatives
The environmental impact of carbon credit programs depends on how they are implemented. When done correctly, these initiatives can fund renewable energy projects, reforestation efforts, and other activities that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, if not properly regulated, they can lead to double-counting of emissions reductions or the support of projects with minimal environmental benefits. Tech giants have the opportunity to set a high standard for accountability and transparency in this area.
See Also Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin?
Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin?Economic Implications of the Carbon Credit Alliance
The collaboration of tech giants in the carbon credit market has significant economic implications. By pooling their resources, these companies can drive down the cost of carbon credits, making them more accessible to other industries. This could stimulate innovation and investment in sustainable technologies. On the other hand, their dominance could lead to market distortions, where smaller companies struggle to compete. Policymakers must carefully monitor this dynamic to ensure a fair and competitive market.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Carbon Credits | Permits allowing emission of a set amount of CO2. |
| Tech Giants Involved | Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and others. |
| Goals | Achieve carbon neutrality or negativity. |
| Challenges | Lack of standardization, high costs, and greenwashing. |
| Economic Impact | Potential to lower costs but risk of market monopolization. |
Who makes the most money from carbon credits?
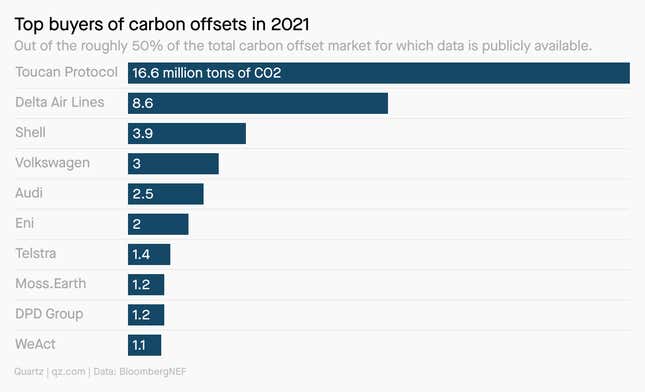
Who Are the Major Players in the Carbon Credit Market?
The carbon credit market is dominated by a mix of corporations, governments, and financial institutions. These entities benefit significantly from trading carbon credits, either by reducing their carbon footprint or by investing in sustainable projects. Below are the key players:
See Also Isometric’s New Carbon Removal Approach
Isometric’s New Carbon Removal Approach- Multinational Corporations: Companies like Shell, BP, and Microsoft purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions and meet regulatory requirements.
- Governments: Countries with large forests or renewable energy projects, such as Brazil and Norway, earn substantial revenue by selling carbon credits.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and investment firms, such as Goldman Sachs and BlackRock, trade carbon credits as part of their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) portfolios.
How Do Corporations Profit from Carbon Credits?
Corporations profit from carbon credits by either reducing emissions or investing in carbon offset projects. These projects can range from reforestation to renewable energy initiatives. Here’s how they benefit:
- Cost Savings: By reducing emissions, companies avoid penalties and save on carbon taxes.
- Revenue Generation: Companies that produce fewer emissions than their allocated limit can sell excess credits to other businesses.
- Brand Enhancement: Participating in carbon credit programs improves a company’s public image and aligns with consumer demand for sustainability.
What Role Do Governments Play in Carbon Credit Earnings?
Governments are pivotal in the carbon credit market, as they regulate and facilitate the trading of credits. They also earn revenue by selling credits from national projects. Key points include:
- Regulation: Governments set emission caps and create frameworks for carbon trading.
- Revenue from Projects: Countries with large-scale renewable energy or conservation projects sell credits internationally.
- International Agreements: Participation in global agreements like the Paris Agreement allows governments to trade credits on a larger scale.
How Do Financial Institutions Benefit from Carbon Credits?
Financial institutions profit from carbon credits by trading them as financial instruments and investing in green projects. Their involvement includes:
- Trading: Banks and investment firms buy and sell carbon credits on exchanges, earning profits from price fluctuations.
- Investment: They fund renewable energy and conservation projects, which generate carbon credits as a return on investment.
- ESG Compliance: Carbon credits help financial institutions meet ESG criteria, attracting socially responsible investors.
What Are the Most Profitable Carbon Credit Projects?
Certain types of carbon credit projects are more profitable due to their scalability and impact. These include:
- Renewable Energy: Wind, solar, and hydroelectric projects generate a high volume of carbon credits.
- Reforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas creates long-term carbon sequestration opportunities.
- Waste Management: Projects that capture methane from landfills or agricultural waste are highly lucrative.
Who gets the money for carbon credits?

Who Receives Revenue from Carbon Credits?
The revenue from carbon credits is typically distributed among various stakeholders involved in projects that reduce or offset greenhouse gas emissions. These stakeholders include:
- Project Developers: Companies or organizations that implement emission reduction projects, such as renewable energy installations or reforestation efforts, receive a significant portion of the revenue.
- Local Communities: In many cases, communities hosting these projects benefit financially through job creation, infrastructure development, or direct payments.
- Governments: Some governments collect taxes or fees from carbon credit transactions, which can be reinvested in environmental initiatives or public services.
- Brokers and Traders: Intermediaries who facilitate the buying and selling of carbon credits earn commissions or fees for their services.
- Investors: Individuals or entities that fund carbon offset projects may receive returns on their investments through the sale of credits.
How Are Carbon Credit Funds Allocated?
The allocation of funds from carbon credits depends on the type of project and the agreements in place. Key allocation methods include:
- Project Costs: A portion of the revenue covers operational and maintenance expenses of the emission reduction project.
- Profit Sharing: Developers and investors often share profits based on predefined agreements.
- Community Benefits: Funds are allocated to support local communities, ensuring they gain from the project's success.
- Administrative Fees: A percentage is used to cover administrative and verification costs.
- Reinvestment: Some funds are reinvested into new or existing environmental projects to sustain long-term impact.
What Role Do Governments Play in Carbon Credit Revenue?
Governments play a crucial role in the carbon credit market by:
- Regulating Markets: Establishing frameworks and standards for carbon credit issuance and trading.
- Taxation: Imposing taxes or fees on carbon credit transactions to generate public revenue.
- Subsidies: Providing financial support to encourage the development of emission reduction projects.
- Policy Development: Creating policies that incentivize businesses and individuals to participate in carbon offset programs.
- Monitoring and Verification: Ensuring the integrity and transparency of carbon credit projects.
How Do Local Communities Benefit from Carbon Credits?
Local communities benefit from carbon credits in several ways, including:
- Economic Opportunities: Job creation in sectors like renewable energy, forestry, and agriculture.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in roads, schools, and healthcare facilities funded by carbon credit revenue.
- Environmental Improvements: Enhanced air and water quality due to reduced emissions and sustainable practices.
- Direct Payments: Some projects provide direct financial compensation to community members.
- Capacity Building: Training and education programs to empower communities to manage and sustain projects.
What Are the Challenges in Distributing Carbon Credit Revenue?
Distributing revenue from carbon credits faces several challenges, such as:
- Transparency Issues: Ensuring that funds are allocated fairly and without corruption.
- Complex Agreements: Navigating the legal and financial complexities of revenue-sharing contracts.
- Equity Concerns: Addressing disparities in how benefits are distributed among stakeholders.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in carbon credit prices can impact revenue stability.
- Verification Costs: High costs associated with monitoring and verifying emission reductions can reduce net revenue.
Who approves carbon credits?

What Are Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are tradable certificates that represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. They are part of a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for achieving reductions in emissions.
- Each credit typically permits the emission of one ton of carbon dioxide.
- They are used by companies and governments to offset their emissions.
- Credits can be bought and sold in carbon markets.
Who Issues Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are issued by regulatory bodies or independent organizations that certify the reduction of emissions. These entities ensure that the projects meet specific environmental standards and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases.
- Regulatory bodies like the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Independent organizations such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and Gold Standard.
- National governments under cap-and-trade systems.
What Is the Role of Verification in Carbon Credits?
Verification is a critical step in the approval of carbon credits. It involves an independent assessment to ensure that the emission reductions are real, measurable, and permanent. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity of the carbon market.
- Verification ensures that projects meet international standards.
- It involves rigorous monitoring and reporting of emission reductions.
- Verified credits are more trustworthy and valuable in the market.
How Are Carbon Credits Approved?
Carbon credits are approved through a multi-step process that includes project development, validation, verification, and issuance. This process ensures that the credits are legitimate and contribute to actual emission reductions.
- Project developers submit detailed plans for emission reduction projects.
- Independent validators assess the project's feasibility and adherence to standards.
- After implementation, verifiers confirm the achieved reductions before credits are issued.
What Are the Standards for Carbon Credit Approval?
Standards for carbon credit approval are set by various international and national bodies to ensure consistency and credibility. These standards define the criteria for project eligibility, measurement methodologies, and verification processes.
- Standards like the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) under the UNFCCC.
- Voluntary standards such as the Climate, Community & Biodiversity Standards (CCBS).
- National standards in countries with emission trading systems.
Who is the largest supplier of carbon credits?

The largest supplier of carbon credits is South Pole, a leading developer of emission reduction projects globally. South Pole has been instrumental in creating and managing projects that generate carbon credits, helping organizations offset their carbon footprints. They work across various sectors, including renewable energy, forestry, and sustainable agriculture, to deliver high-quality carbon credits.
What Are Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are permits that allow the holder to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit typically equals one ton of CO2. These credits are part of cap-and-trade systems designed to reduce emissions.
- Cap-and-trade systems set a limit on emissions and allow companies to buy or sell allowances.
- Carbon credits can be generated through projects that reduce or remove emissions, such as reforestation or renewable energy initiatives.
- They are traded on carbon markets, enabling companies to offset their emissions by purchasing credits from others.
How Does South Pole Generate Carbon Credits?
South Pole generates carbon credits by developing and managing projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gas emissions. These projects are verified by third-party organizations to ensure their credibility.
- Renewable energy projects, such as wind farms and solar installations, replace fossil fuel-based energy sources.
- Forest conservation and reforestation projects capture CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Sustainable agriculture practices reduce emissions from farming activities.
Why Are Carbon Credits Important?
Carbon credits play a crucial role in combating climate change by incentivizing emission reductions and funding sustainable projects.
- They provide a financial mechanism for companies to offset their unavoidable emissions.
- Carbon credits fund projects that might not otherwise be economically viable, such as renewable energy in developing countries.
- They encourage innovation in low-carbon technologies and practices.
What Makes South Pole a Leader in Carbon Credits?
South Pole stands out due to its extensive experience, global reach, and commitment to high-quality projects.
- They have developed over 1,000 projects across more than 50 countries.
- Their projects are certified under rigorous standards like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and the Gold Standard.
- South Pole works with a diverse range of clients, from multinational corporations to small businesses.
What Are the Challenges in the Carbon Credit Market?
Despite its benefits, the carbon credit market faces several challenges that need to be addressed.
- Lack of transparency in some projects can lead to issues like double-counting or overestimation of emission reductions.
- The market is fragmented, with varying standards and regulations across regions.
- Ensuring the additionality of projects—meaning the emissions reductions would not have occurred without the carbon credit funding—is critical but challenging.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are carbon credits and why are tech giants investing in them?
Carbon credits are permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One credit typically equals one ton of carbon dioxide. Tech giants are investing in carbon credits as part of their broader sustainability strategies to offset their carbon footprints. By purchasing these credits, they can fund environmental projects that reduce emissions elsewhere, effectively balancing out their own emissions. This move is also seen as a way to enhance their corporate image and meet regulatory requirements.
How do tech companies benefit from joining forces for carbon credits?
By joining forces, tech companies can pool resources and expertise to invest in larger, more impactful environmental projects. This collaboration allows them to achieve economies of scale, making it more cost-effective to purchase carbon credits. Additionally, working together can lead to the development of more standardized and transparent systems for tracking and verifying carbon credits, which can help build trust and credibility in the market. This collective effort also sends a strong message about the industry's commitment to combating climate change.
What challenges do tech giants face in implementing carbon credit initiatives?
One of the main challenges is ensuring the integrity and transparency of carbon credits. There have been instances of fraud and double-counting in the carbon credit market, which can undermine the effectiveness of these initiatives. Tech giants also face the challenge of accurately measuring their carbon footprints and ensuring that the projects they fund genuinely reduce emissions. Additionally, there is the risk of public skepticism, with critics arguing that carbon credits allow companies to buy their way out of making real changes to their operations.
What impact could this collaboration have on the broader carbon credit market?
The involvement of tech giants could significantly boost the carbon credit market by increasing demand and driving innovation. Their participation could lead to the development of more sophisticated technologies for monitoring and verifying carbon credits, making the market more efficient and reliable. Furthermore, their influence could encourage other industries to adopt similar practices, potentially leading to a more widespread reduction in global emissions. However, it is crucial that these efforts are accompanied by genuine reductions in emissions and not just used as a public relations tool.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles