The Congo Basin, home to the world’s second-largest tropical rainforest, plays a critical role in global climate regulation and biodiversity conservation. However, funding carbon projects in this region remains a significant challenge, despite their potential to deliver substantial environmental and social benefits. Raising capital for such initiatives requires innovative strategies that balance investor interests, local community needs, and long-term sustainability. This article explores the most effective approaches to securing funding for carbon projects in the Congo Basin, examining the role of public-private partnerships, carbon credit markets, and international climate finance mechanisms. By addressing these challenges, stakeholders can unlock the region’s potential as a global leader in climate mitigation.

- Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin
- What is being done to help the Congo Basin?
- What is the Congo Basin Blue Fund?
- How much carbon does the Congo Basin absorb?
- What are the resources in the Congo Basin?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What are the most effective funding sources for carbon projects in the Congo Basin?
- How can carbon credits be leveraged to raise capital for these projects?
- What role do partnerships play in financing carbon projects in the Congo Basin?
- What challenges do carbon projects in the Congo Basin face when raising capital?
Best Way to Raise Capital for Carbon Projects in the Congo Basin
Raising capital for carbon projects in the Congo Basin requires a strategic approach that combines innovative financing mechanisms, strong partnerships, and effective communication of the project's environmental and social benefits. The Congo Basin, often referred to as the lungs of Africa, is a critical region for global carbon sequestration, making it a prime location for carbon offset projects. However, securing funding for such initiatives can be challenging due to the region's complex socio-economic and political landscape. Below, we explore the best strategies to attract investment for these vital projects.
1. Leveraging Carbon Credits and Offsetting Mechanisms
One of the most effective ways to raise capital for carbon projects in the Congo Basin is through the sale of carbon credits. These credits are generated by projects that reduce or sequester greenhouse gas emissions, and they can be sold to companies or individuals looking to offset their carbon footprint. By participating in established carbon markets, such as the Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) or compliance markets like the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), projects can attract significant funding. Additionally, third-party verification of carbon credits by organizations like Verra or Gold Standard ensures credibility and increases investor confidence.
See Also Isometric’s New Carbon Removal Approach
Isometric’s New Carbon Removal Approach2. Building Partnerships with International Organizations
Collaborating with international organizations such as the World Bank, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), or Global Environment Facility (GEF) can provide access to grants, technical expertise, and funding opportunities. These organizations often prioritize projects that align with global climate goals, such as reducing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use. By aligning carbon projects in the Congo Basin with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), stakeholders can tap into a broader pool of resources and support.
3. Engaging Private Sector Investors
The private sector plays a crucial role in financing carbon projects. Impact investors, venture capitalists, and corporate sustainability funds are increasingly interested in projects that deliver both environmental and financial returns. To attract private investment, carbon projects must demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI) and a robust risk management strategy. Highlighting the Congo Basin's unique biodiversity and its potential for large-scale carbon sequestration can also appeal to investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
4. Utilizing Blended Finance Models
Blended finance combines public and private funding to de-risk investments and make them more attractive to private investors. For example, a carbon project in the Congo Basin could receive initial funding from a development bank, which would then leverage additional private capital. This approach reduces the financial burden on any single investor and encourages broader participation. Blended finance models are particularly effective in regions with high perceived risks, such as the Congo Basin, as they provide a safety net for investors.
See Also Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050: How Sustainable Agriculture Is Leading the Charge
Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050: How Sustainable Agriculture Is Leading the Charge5. Promoting Community Involvement and Benefits
Ensuring that local communities benefit from carbon projects is essential for their long-term success. By involving communities in project design and implementation, stakeholders can build trust and secure local support. Revenue-sharing models, where a portion of the income from carbon credits is reinvested into community development, can create a sense of ownership and incentivize conservation efforts. Additionally, projects that provide alternative livelihoods, such as sustainable agriculture or eco-tourism, can reduce reliance on deforestation and enhance the project's overall impact.
| Strategy | Key Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Credits | Access to global markets, high demand for offsets | Requires rigorous verification and monitoring |
| International Partnerships | Access to grants and technical expertise | Complex application processes |
| Private Sector Engagement | Potential for large-scale funding | High competition for investor attention |
| Blended Finance | Reduces risk for private investors | Requires coordination between multiple stakeholders |
| Community Involvement | Enhances project sustainability and local support | Requires long-term commitment and resources |
What is being done to help the Congo Basin?
Conservation Initiatives in the Congo Basin
Several conservation initiatives are being implemented to protect the Congo Basin, one of the world's most critical ecosystems. These efforts focus on preserving biodiversity, combating deforestation, and supporting sustainable development. Key actions include:
See Also The Role of CO2 Direct Air Capture in Combating Climate Change: A Path Toward Sustainable Agriculture and Energy
The Role of CO2 Direct Air Capture in Combating Climate Change: A Path Toward Sustainable Agriculture and Energy- Establishing protected areas and national parks to safeguard wildlife habitats.
- Promoting community-based conservation programs to involve local populations in protecting their environment.
- Implementing anti-poaching measures to protect endangered species like elephants and gorillas.
International Funding and Partnerships
International organizations and governments are providing financial support and forming partnerships to aid the Congo Basin. These collaborations aim to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable practices. Examples include:
- The Central African Forest Initiative (CAFI), which funds projects to reduce deforestation and improve forest management.
- Partnerships with organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the United Nations to support conservation efforts.
- Funding from the European Union and other donors to enhance local capacity for environmental protection.
Sustainable Development Programs
Efforts are being made to balance conservation with economic development in the Congo Basin. Sustainable development programs aim to improve livelihoods while preserving natural resources. Key initiatives include:
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices to reduce deforestation and soil degradation.
- Supporting eco-tourism to generate income while protecting wildlife and forests.
- Encouraging the use of renewable energy sources to minimize environmental impact.
Research and Monitoring Efforts
Scientific research and monitoring are critical to understanding and protecting the Congo Basin. These efforts help track environmental changes and inform conservation strategies. Key activities include:
- Conducting biodiversity surveys to monitor species populations and health.
- Using satellite technology to track deforestation and land-use changes.
- Collaborating with local and international researchers to study the impacts of climate change on the region.
Policy and Legal Frameworks
Strengthening policy and legal frameworks is essential for effective conservation in the Congo Basin. Governments and organizations are working to create and enforce laws that protect the environment. Key measures include:
- Developing forest governance policies to regulate logging and land use.
- Enforcing wildlife protection laws to combat illegal hunting and trade.
- Promoting transboundary cooperation among countries sharing the Congo Basin to ensure coordinated conservation efforts.
What is the Congo Basin Blue Fund?
The Congo Basin Blue Fund is an innovative financial mechanism designed to promote sustainable development and environmental conservation in the Congo Basin region. It focuses on leveraging the region's vast water resources to support economic growth, poverty reduction, and climate resilience. The fund aims to address critical challenges such as deforestation, biodiversity loss, and water management while fostering community engagement and regional cooperation.
Objectives of the Congo Basin Blue Fund
The primary objectives of the Congo Basin Blue Fund are:
- Promote sustainable water resource management to ensure long-term availability for communities and ecosystems.
- Support climate change adaptation by enhancing the resilience of local populations and natural habitats.
- Encourage economic development through projects that create jobs and improve livelihoods while preserving the environment.
Key Features of the Congo Basin Blue Fund
The Congo Basin Blue Fund is characterized by several key features:
- Multi-stakeholder involvement, including governments, NGOs, and private sector partners.
- Focus on blue economy initiatives, such as sustainable fisheries, eco-tourism, and renewable energy.
- Transparent governance to ensure accountability and effective use of resources.
Impact of the Congo Basin Blue Fund
The Congo Basin Blue Fund has the potential to create significant positive impacts:
- Environmental benefits, including reduced deforestation and improved biodiversity conservation.
- Social benefits, such as improved access to clean water and enhanced community resilience.
- Economic benefits, including job creation and increased investment in sustainable industries.
Challenges Facing the Congo Basin Blue Fund
Despite its potential, the Congo Basin Blue Fund faces several challenges:
- Funding gaps due to limited financial commitments from stakeholders.
- Political instability in some regions of the Congo Basin, which can hinder implementation.
- Coordination difficulties among diverse stakeholders with varying priorities.
How much carbon does the Congo Basin absorb?
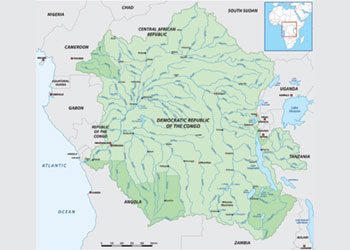
The Congo Basin, one of the world's largest tropical rainforests, plays a critical role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It is estimated that the Congo Basin absorbs approximately 1.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide annually, making it one of the most significant carbon sinks on the planet. This vast rainforest covers over 1.5 million square miles across six Central African countries and is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna that contribute to its carbon sequestration capabilities.
How Does the Congo Basin Absorb Carbon?
The Congo Basin absorbs carbon through its dense vegetation and soil. Here’s how it works:
- Photosynthesis: Trees and plants in the Congo Basin absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, converting it into oxygen and storing carbon in their biomass.
- Soil Carbon Storage: The forest floor and soil in the Congo Basin store significant amounts of carbon, which is retained through decomposition and organic matter accumulation.
- Peatlands: The Congo Basin contains extensive peatlands, which are waterlogged areas that store large amounts of carbon over thousands of years.
Why Is the Congo Basin a Critical Carbon Sink?
The Congo Basin is vital for global climate regulation due to its immense carbon absorption capacity. Key reasons include:
- Size and Density: Its vast area and dense vegetation allow it to store more carbon than many other forests.
- Biodiversity: The high biodiversity supports complex ecosystems that enhance carbon sequestration.
- Climate Impact: By absorbing carbon, the Congo Basin helps mitigate the effects of climate change, such as rising global temperatures.
How Does Deforestation Affect the Congo Basin's Carbon Absorption?
Deforestation poses a significant threat to the Congo Basin's ability to absorb carbon. The impacts include:
- Reduced Carbon Storage: Cutting down trees reduces the forest's capacity to store carbon, releasing it back into the atmosphere.
- Soil Degradation: Deforestation leads to soil erosion, which diminishes the soil's ability to retain carbon.
- Loss of Peatlands: Draining peatlands for agriculture or development releases stored carbon, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
What Are the Main Threats to the Congo Basin's Carbon Sequestration?
Several factors threaten the Congo Basin's ability to absorb and store carbon:
- Illegal Logging: Unregulated logging activities reduce forest cover and disrupt ecosystems.
- Agricultural Expansion: Converting forests into farmland reduces carbon storage and increases emissions.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns can stress the forest, reducing its carbon absorption efficiency.
How Can the Congo Basin's Carbon Absorption Be Protected?
Protecting the Congo Basin requires coordinated efforts at local, national, and international levels. Key strategies include:
- Sustainable Forestry: Implementing practices that balance logging with forest regeneration.
- Conservation Programs: Establishing protected areas to prevent deforestation and habitat loss.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts to ensure long-term sustainability.
What are the resources in the Congo Basin?

Mineral Resources in the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin is rich in mineral resources, making it one of the most resource-dense regions in the world. Key minerals found here include:
- Copper: Widely mined in the Katanga region, it is a major export commodity.
- Cobalt: The Congo Basin holds a significant portion of the world's cobalt reserves, essential for battery production.
- Diamonds: The region is a leading producer of industrial and gem-quality diamonds.
- Gold: Found in various parts of the basin, it supports both large-scale and artisanal mining.
- Coltan: A critical mineral used in electronics, primarily sourced from the eastern Congo.
Forest Resources in the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin is home to the second-largest tropical rainforest in the world, providing forest resources that are vital for both local and global ecosystems. Key resources include:
- Timber: High-value hardwoods like mahogany and teak are harvested sustainably and unsustainably.
- Medicinal Plants: The forest is a source of traditional medicines used by local communities.
- Non-Timber Forest Products: Includes fruits, nuts, and resins that support local livelihoods.
- Carbon Sequestration: The forest plays a critical role in absorbing carbon dioxide, mitigating climate change.
- Biodiversity: The forest supports countless species, many of which are endemic to the region.
Water Resources in the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin is endowed with abundant water resources, primarily from the Congo River and its tributaries. These resources are crucial for various purposes:
- Hydropower: The Congo River has immense potential for generating electricity, with projects like the Inga Dam.
- Fisheries: The river and its tributaries support a thriving fishing industry, providing food and income.
- Transportation: The river serves as a major transport route for goods and people.
- Irrigation: Water from the basin supports agricultural activities in the region.
- Drinking Water: Millions of people rely on the basin's water for daily consumption.
Agricultural Resources in the Congo Basin
The fertile soils and favorable climate of the Congo Basin support a variety of agricultural resources. Key agricultural products include:
- Cassava: A staple food crop widely cultivated in the region.
- Maize: Grown extensively for both local consumption and export.
- Palm Oil: Produced in large quantities, it is a major export commodity.
- Cocoa: The basin is a significant producer of cocoa beans for the global market.
- Rubber: Harvested from rubber trees, it supports both local and international industries.
Wildlife Resources in the Congo Basin
The Congo Basin is a biodiversity hotspot, hosting a wide range of wildlife resources. Notable examples include:
- Gorillas: Both mountain and lowland gorillas are found in the region.
- Elephants: Forest elephants are a key species in the basin's ecosystem.
- Okapi: A unique mammal endemic to the Congo Basin.
- Birds: The region is home to numerous bird species, many of which are rare or endangered.
- Reptiles and Amphibians: The basin supports a diverse range of reptiles and amphibians, including crocodiles and frogs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the most effective funding sources for carbon projects in the Congo Basin?
Carbon projects in the Congo Basin can secure funding through a variety of sources, including international climate funds, private investors, and government grants. International organizations such as the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and the World Bank often provide financial support for initiatives aimed at reducing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use. Additionally, carbon credit markets offer a viable revenue stream by allowing projects to sell verified carbon offsets to companies and individuals looking to mitigate their carbon footprint.
How can carbon credits be leveraged to raise capital for these projects?
Carbon credits are a powerful tool for raising capital, as they provide a tangible financial incentive for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Projects in the Congo Basin can generate credits by implementing activities such as reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable forest management. These credits can then be sold on voluntary carbon markets or through compliance markets, depending on the project's certification and the demand for offsets. Partnering with reputable carbon standards like Verra or Gold Standard ensures credibility and attracts more investors.
What role do partnerships play in financing carbon projects in the Congo Basin?
Partnerships are crucial for the success of carbon projects in the Congo Basin. Collaborating with local communities, NGOs, and international organizations can provide not only financial resources but also technical expertise and local knowledge. For example, partnerships with indigenous groups ensure that projects are culturally sensitive and socially inclusive, while alliances with research institutions can enhance monitoring and verification processes. These collaborations also increase the project's visibility, making it more attractive to potential investors.
What challenges do carbon projects in the Congo Basin face when raising capital?
Despite their potential, carbon projects in the Congo Basin often face significant challenges in raising capital. These include high upfront costs, complex certification processes, and political instability in the region. Additionally, the lack of infrastructure and technical capacity can deter investors. To overcome these barriers, projects must demonstrate transparency, long-term viability, and a clear plan for community engagement. Building trust with stakeholders and showcasing measurable environmental and social impacts are also key to securing funding.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles