Carbon emissions trading has emerged as a pivotal mechanism in the global effort to combat climate change. By creating a market for carbon credits, this system incentivizes industries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions while promoting sustainable practices. This article delves into the intricacies of carbon emissions trading, examining its economic principles, regulatory frameworks, and real-world applications. Through a comprehensive analysis, we explore the effectiveness of this market-based approach in achieving emission reduction targets, its impact on businesses, and the challenges it faces. Understanding the dynamics of carbon trading is essential for policymakers, businesses, and stakeholders committed to fostering a greener, more sustainable future.

Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis: Understanding the Mechanisms and Impacts
Carbon emissions trading, also known as cap-and-trade, is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing emissions. This system sets a cap on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted by all participating entities. Companies or other groups are issued emission permits and are required to hold an equivalent number of allowances (or credits) which represent the right to emit a specific amount. The total amount of allowances cannot exceed the cap, limiting total emissions to that level. Companies that need to increase their emission allowance must buy credits from those who pollute less, creating a financial incentive to reduce emissions.
1. The Basics of Carbon Emissions Trading
Carbon emissions trading is fundamentally about setting a limit on emissions and allowing the market to determine a price for those emissions. This system is designed to reduce emissions in a cost-effective and flexible manner. The cap is typically reduced over time, aiming to decrease total emissions. The trading aspect allows companies that can reduce emissions at lower costs to sell their extra allowances to companies facing higher reduction costs, thus optimizing the overall cost of emission reductions.
See Also Carbon Credit NFTs: An Increasingly Popular Real-World Use Case That You Should Know About!
Carbon Credit NFTs: An Increasingly Popular Real-World Use Case That You Should Know About!2. Key Components of a Carbon Trading System
A carbon trading system consists of several key components:
- Cap: The maximum level of emissions allowed.
- Allowances: Permits that allow the holder to emit a certain amount of CO2.
- Trading: The buying and selling of allowances between companies.
- Compliance: Mechanisms to ensure that companies adhere to the rules, including penalties for non-compliance.
3. Benefits of Carbon Emissions Trading
Carbon emissions trading offers several benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: It provides a flexible way for companies to meet emission reduction targets at the lowest possible cost.
- Innovation: Encourages innovation in clean technology as companies seek to reduce emissions and sell excess allowances.
- Economic Efficiency: Allocates resources efficiently by allowing the market to determine the price of emissions.
4. Challenges in Carbon Emissions Trading
Despite its benefits, carbon emissions trading faces several challenges:
- Market Volatility: Prices for carbon credits can be highly volatile, making it difficult for companies to plan long-term investments.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in policy or regulation can impact the market significantly.
- Leakage: There is a risk that emissions reductions in one area could lead to increased emissions elsewhere, undermining the overall effectiveness of the system.
 How Can I Make Money With Carbon Credits?
How Can I Make Money With Carbon Credits?5. Global Examples of Carbon Emissions Trading Systems
Several regions and countries have implemented carbon emissions trading systems:
- European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS): The largest multi-country, multi-sector greenhouse gas emissions trading system in the world.
- California Cap-and-Trade Program: A key element of California's strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- China National Emissions Trading Scheme: The world's largest carbon market, covering more than 4 billion tonnes of CO2 annually.
| System | Region | Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| EU ETS | European Union | Multiple sectors |
| California Cap-and-Trade | California, USA | Multiple sectors |
| China National ETS | China | Power sector initially |
How do you trade carbon emissions?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carbontrade.asp-final-e4d2e4fa04db4679851cb60c873fac86.png)
What is Carbon Trading?
Carbon trading, also known as emissions trading, is a market-based approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It allows companies or countries to buy and sell carbon credits, which represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. This system incentivizes emission reductions by putting a price on carbon.
See Also CFTC Charges Former CEO of Carbon Credit Project
CFTC Charges Former CEO of Carbon Credit Project- Cap-and-Trade Systems: Governments set a cap on total emissions and issue allowances that companies can trade.
- Carbon Offsets: Companies can invest in projects that reduce emissions elsewhere to offset their own emissions.
- Voluntary Markets: Businesses or individuals can purchase carbon credits voluntarily to reduce their carbon footprint.
How Does Carbon Trading Work?
Carbon trading operates through a system where emission allowances are allocated or auctioned. Companies that reduce their emissions below their allowance can sell their excess credits to others who need them. This creates a financial incentive for companies to innovate and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Allocation: Governments or regulatory bodies distribute emission allowances to companies.
- Trading: Companies buy or sell allowances on a carbon market.
- Compliance: At the end of a compliance period, companies must surrender enough allowances to cover their emissions.
Types of Carbon Markets
There are two main types of carbon markets: compliance markets and voluntary markets. Compliance markets are regulated by governments and require companies to meet specific emission targets. Voluntary markets allow businesses and individuals to purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions voluntarily.
- Compliance Markets: Operate under legal frameworks like the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).
- Voluntary Markets: Include initiatives like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard.
- Hybrid Markets: Some markets combine elements of both compliance and voluntary systems.
Key Players in Carbon Trading
The carbon trading ecosystem involves various stakeholders, including governments, corporations, financial institutions, and project developers. Each plays a critical role in ensuring the system functions effectively.
- Governments: Set emission caps and regulate the market.
- Corporations: Buy and sell carbon credits to meet compliance or sustainability goals.
- Financial Institutions: Facilitate trading and provide liquidity to the market.
- Project Developers: Create carbon offset projects like reforestation or renewable energy initiatives.
Benefits and Challenges of Carbon Trading
Carbon trading offers several benefits, such as cost-effective emission reductions and encouraging innovation. However, it also faces challenges like market volatility and ensuring transparency.
- Benefits: Provides flexibility for companies to meet emission targets, promotes green investments, and reduces overall emissions.
- Challenges: Requires robust monitoring and verification, can be subject to fraud, and may face political resistance.
- Future Outlook: As global climate goals become more ambitious, carbon trading is expected to expand and evolve.
What is the difference between carbon trading and emissions trading?

What is Carbon Trading?
Carbon trading is a market-based system designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by allowing companies or countries to buy and sell carbon credits. Each credit represents the right to emit one ton of carbon dioxide or an equivalent amount of other greenhouse gases. This system incentivizes emission reductions by assigning a monetary value to carbon emissions, encouraging businesses to adopt cleaner technologies or practices.
- Carbon credits are issued to entities that reduce their emissions below a set limit.
- Entities exceeding their emission limits must purchase additional credits from those with surplus.
- The goal is to create a financial incentive for reducing emissions while maintaining economic flexibility.
What is Emissions Trading?
Emissions trading is a broader concept that includes the trading of permits for various types of pollutants, not just carbon dioxide. It operates on the same principle as carbon trading but applies to a wider range of emissions, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other harmful substances. This system is often used to regulate air quality and reduce environmental pollution.
- Emissions allowances are allocated to companies, allowing them to emit a specific amount of pollutants.
- Companies can trade these allowances, creating a market for pollution reduction.
- The system aims to achieve environmental targets at the lowest possible cost.
Key Differences Between Carbon Trading and Emissions Trading
The primary difference lies in the scope of the pollutants covered. Carbon trading focuses exclusively on greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, while emissions trading encompasses a wider range of pollutants. Additionally, carbon trading is often implemented on a global or regional scale, whereas emissions trading can be tailored to address specific local or national environmental concerns.
- Carbon trading targets greenhouse gases, while emissions trading addresses multiple pollutants.
- Carbon trading is commonly used in international climate agreements, such as the Kyoto Protocol.
- Emissions trading systems are often designed to meet local air quality standards.
How Carbon Trading Works
In a carbon trading system, governments or regulatory bodies set a cap on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted. Companies are allocated or can purchase carbon credits, which represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide. If a company reduces its emissions below its allocated limit, it can sell its surplus credits to other companies that need them.
- A cap-and-trade system is established to limit total emissions.
- Companies that reduce emissions can profit by selling their excess credits.
- This system encourages innovation and investment in cleaner technologies.
How Emissions Trading Works
Emissions trading operates similarly to carbon trading but applies to a broader range of pollutants. Regulatory authorities set a cap on the total emissions of specific pollutants and issue permits or allowances to companies. Companies that reduce their emissions below their allocated limit can sell their surplus allowances to others, creating a financial incentive for pollution reduction.
- Regulators set a cap on total emissions for specific pollutants.
- Companies receive or purchase emissions allowances.
- Surplus allowances can be traded, promoting cost-effective pollution control.
What is carbon emission analysis?
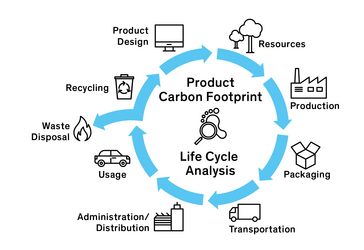
What is Carbon Emission Analysis?
Carbon emission analysis is the process of measuring and evaluating the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) released into the atmosphere by human activities, such as industrial processes, transportation, and energy production. This analysis helps organizations and governments understand their environmental impact, identify sources of emissions, and develop strategies to reduce their carbon footprint. It is a critical tool in combating climate change and achieving sustainability goals.
Why is Carbon Emission Analysis Important?
Carbon emission analysis is essential for several reasons:
- Climate Change Mitigation: It helps identify the primary sources of emissions, enabling targeted actions to reduce them.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many governments require businesses to report their emissions to comply with environmental regulations.
- Sustainability Goals: Organizations use this analysis to set and track progress toward reducing their carbon footprint.
- Public Accountability: Transparent reporting builds trust with stakeholders and consumers.
- Cost Savings: Identifying inefficiencies can lead to reduced energy consumption and operational costs.
How is Carbon Emission Analysis Conducted?
The process of conducting carbon emission analysis involves several steps:
- Data Collection: Gathering information on energy use, fuel consumption, and other activities that produce emissions.
- Emission Calculation: Using standardized methods and tools to quantify emissions, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol.
- Source Identification: Determining which activities or processes contribute the most to emissions.
- Reporting: Documenting findings in a clear and transparent manner, often for regulatory or public disclosure.
- Action Planning: Developing strategies to reduce emissions based on the analysis results.
What Tools are Used in Carbon Emission Analysis?
Several tools and methodologies are employed in carbon emission analysis:
- Carbon Calculators: Software tools that estimate emissions based on input data.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Evaluates emissions across the entire lifecycle of a product or service.
- Emission Factors: Standardized values used to convert activity data into emissions.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite data to monitor large-scale emissions, such as deforestation or industrial activity.
- Blockchain Technology: Emerging tools for transparent and secure emission tracking.
What are the Challenges in Carbon Emission Analysis?
Conducting carbon emission analysis comes with several challenges:
- Data Accuracy: Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to unreliable results.
- Complexity: Emissions from indirect sources, such as supply chains, are difficult to measure.
- Cost: Advanced tools and methodologies can be expensive to implement.
- Regulatory Variability: Different regions have varying standards and reporting requirements.
- Technological Limitations: Some emission sources are hard to monitor with current technology.
How is carbon trading measured?

What is Carbon Trading?
Carbon trading is a market-based system designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by allowing companies or countries to buy and sell carbon credits. Each credit represents the right to emit one ton of carbon dioxide or an equivalent amount of other greenhouse gases. The system operates under a cap-and-trade mechanism, where a cap is set on total emissions, and entities can trade allowances to stay within the limit.
- Cap-and-trade systems set a maximum limit on emissions.
- Carbon credits are issued to entities that reduce emissions below their allocated limit.
- Entities exceeding their limit must purchase additional credits from others.
How Are Carbon Credits Measured?
Carbon credits are measured in metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e). This unit accounts for the global warming potential of different greenhouse gases, such as methane or nitrous oxide, by converting them into equivalent amounts of CO2. Accurate measurement is critical to ensure the integrity of the carbon market.
- CO2e is the standard unit for measuring carbon credits.
- Emissions are calculated using monitoring tools and reporting protocols.
- Third-party verification ensures the accuracy of emission reductions.
What Tools Are Used to Measure Emissions?
Emissions are measured using a combination of direct monitoring and emission factors. Direct monitoring involves sensors and meters that track emissions in real-time, while emission factors estimate emissions based on activity data, such as fuel consumption or production levels.
- Direct monitoring uses sensors to measure emissions at the source.
- Emission factors estimate emissions based on activity data.
- Advanced tools like satellite imaging are also used for large-scale monitoring.
What Role Do Standards Play in Carbon Trading?
Standards ensure consistency and transparency in carbon trading. Organizations like the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) and Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) provide guidelines for measuring, reporting, and verifying emissions. These standards help maintain trust in the carbon market.
- CDM and VCS are key standards for carbon trading.
- Standards define methodologies for calculating emissions.
- They require third-party audits to verify emission reductions.
How Are Carbon Offsets Measured?
Carbon offsets are measured by quantifying the reduction or removal of greenhouse gases achieved through specific projects, such as reforestation or renewable energy initiatives. The measurement process involves baseline calculations to determine what emissions would have been without the project and additionality to ensure the project would not have happened otherwise.
- Baseline calculations estimate emissions without the project.
- Additionality ensures the project provides real emission reductions.
- Projects must meet strict criteria to qualify as valid offsets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis?
Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis refers to the process of evaluating and interpreting data related to carbon trading markets. These markets operate on the principle of cap-and-trade, where a limit (cap) is set on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted by all participating entities. Companies or organizations are allocated or can purchase emission allowances, which they can trade with others. The analysis involves assessing market trends, pricing mechanisms, regulatory impacts, and the effectiveness of these systems in reducing overall carbon emissions. It plays a crucial role in helping businesses and policymakers make informed decisions to achieve climate goals.
Why is Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis important for businesses?
Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis is vital for businesses because it helps them understand their carbon footprint and the financial implications of their emissions. By analyzing carbon trading markets, companies can identify cost-effective strategies to reduce emissions, such as purchasing additional allowances or investing in cleaner technologies. Additionally, it enables businesses to stay compliant with environmental regulations and avoid penalties. Moreover, companies that proactively manage their emissions can enhance their reputation, attract environmentally conscious investors, and gain a competitive edge in markets increasingly focused on sustainability.
How does Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis impact global climate goals?
Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis directly impacts global climate goals by providing insights into the effectiveness of carbon trading systems in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By analyzing data from these markets, policymakers can identify gaps, adjust caps, and refine regulations to ensure that emission reduction targets are met. Furthermore, it helps in tracking progress toward international agreements like the Paris Agreement. The analysis also highlights the role of market mechanisms in incentivizing industries to adopt cleaner practices, ultimately contributing to the global effort to mitigate climate change.
What tools and methods are used in Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis?
Carbon Emissions Trading Analysis employs a variety of tools and methods to evaluate market dynamics and emission trends. These include data analytics platforms, which process large datasets to identify patterns and predict future market behavior. Econometric models are used to assess the relationship between carbon prices and external factors like energy costs or regulatory changes. Additionally, lifecycle assessment tools help quantify the emissions associated with specific activities or products. Advanced technologies, such as machine learning and blockchain, are also being integrated to enhance transparency and accuracy in tracking emissions and trades.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles