In recent years, the intersection of blockchain technology and environmental sustainability has given rise to an innovative solution: Carbon Credit NFTs. These digital assets are transforming the way carbon credits are tracked, traded, and utilized, offering a transparent and efficient alternative to traditional systems. By tokenizing carbon credits as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), businesses and individuals can now participate in carbon offsetting with greater accessibility and accountability. As climate change concerns grow, Carbon Credit NFTs are emerging as a powerful tool to incentivize eco-friendly practices and drive global decarbonization efforts. This article explores how this groundbreaking use case is gaining traction and why it matters.

Carbon Credit NFTs: An Increasingly Popular Real-World Use Case That You Should Know About!
What Are Carbon Credit NFTs?
Carbon Credit NFTs are a groundbreaking innovation that combines blockchain technology with environmental sustainability. These NFTs represent a digital certificate for carbon credits, which are tradable permits that allow the holder to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. By tokenizing carbon credits, they become more accessible, transparent, and easier to trade on digital platforms. This fusion of blockchain and carbon credits is revolutionizing how we approach environmental conservation and climate change mitigation.
How Do Carbon Credit NFTs Work?
Carbon Credit NFTs operate by leveraging blockchain technology to create a transparent and immutable record of carbon credit ownership. Each NFT is linked to a specific amount of carbon offset, verified by third-party organizations. These NFTs can be bought, sold, or traded on various platforms, allowing individuals and companies to participate in carbon offsetting more efficiently. The use of smart contracts ensures that transactions are secure and automated, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust in the system.
See Also How Can I Make Money With Carbon Credits?
How Can I Make Money With Carbon Credits?Benefits of Carbon Credit NFTs
The benefits of Carbon Credit NFTs are numerous. They provide transparency by allowing anyone to verify the origin and validity of carbon credits. They also enhance liquidity, making it easier for businesses and individuals to trade carbon credits. Additionally, they promote accessibility, enabling smaller entities to participate in carbon offsetting. The use of blockchain technology also ensures traceability, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of carbon markets.
Challenges and Risks
Despite their potential, Carbon Credit NFTs face several challenges. One major issue is the verification of carbon credits, as not all projects may meet the required standards. There is also the risk of market manipulation and fraud, which can undermine trust in the system. Additionally, the energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work, can offset the environmental benefits of carbon credits. Addressing these challenges is essential for the long-term success of Carbon Credit NFTs.
Future Prospects of Carbon Credit NFTs
The future of Carbon Credit NFTs looks promising, with increasing interest from both the private and public sectors. As more companies commit to net-zero emissions, the demand for carbon credits is expected to rise. Innovations in blockchain technology, such as the adoption of proof-of-stake and other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, could further enhance the sustainability of Carbon Credit NFTs. Moreover, the integration of AI and IoT could improve the accuracy and efficiency of carbon credit verification and trading.
See Also CFTC Charges Former CEO of Carbon Credit Project
CFTC Charges Former CEO of Carbon Credit Project| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Blockchain ensures that all transactions are publicly verifiable. |
| Liquidity | NFTs make it easier to trade carbon credits on digital platforms. |
| Accessibility | Smaller entities can participate in carbon offsetting. |
| Traceability | Blockchain provides an immutable record of carbon credit ownership. |
| Challenges | Verification, market manipulation, and energy consumption are key issues. |
Can you make money from carbon credits?

How Do Carbon Credits Work?
Carbon credits are a market-based tool designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. They represent the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. Companies or individuals can buy and sell these credits to offset their emissions. Here’s how it works:
- Cap-and-Trade Systems: Governments or regulatory bodies set a cap on total emissions and issue a limited number of carbon credits. Companies that reduce their emissions below the cap can sell their excess credits to others.
- Voluntary Markets: Individuals or companies can purchase carbon credits voluntarily to offset their carbon footprint, often to meet sustainability goals or improve their public image.
- Carbon Offset Projects: Credits are generated by projects that reduce or capture emissions, such as reforestation, renewable energy, or methane capture initiatives.
Who Can Profit from Carbon Credits?
Various entities can profit from carbon credits, depending on their role in the market. Here are the key players:
See Also Reducing Carbon Footprint. Does Your Org Care?
Reducing Carbon Footprint. Does Your Org Care?- Project Developers: Companies or organizations that implement emission-reduction projects, such as renewable energy farms or reforestation efforts, can earn credits and sell them.
- Brokers and Traders: Intermediaries who buy and sell carbon credits on behalf of buyers and sellers, earning a commission or profit margin.
- Corporations: Businesses that reduce their emissions below their allocated cap can sell their excess credits for profit.
What Are the Types of Carbon Credit Projects?
Carbon credit projects vary widely and are categorized based on the type of emission reduction or removal they achieve. Here are the main types:
- Renewable Energy Projects: Wind, solar, and hydroelectric power projects that replace fossil fuel-based energy sources.
- Forestry and Land Use: Reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable land management projects that capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Waste Management: Projects that capture methane from landfills or agricultural waste and convert it into energy.
How to Buy and Sell Carbon Credits?
Buying and selling carbon credits involves several steps and platforms. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine whether you need to buy credits to offset emissions or sell credits generated from emission reductions.
- Choose a Market: Decide between compliance markets (regulated by governments) or voluntary markets (for individuals and businesses).
- Use a Broker or Exchange: Work with a broker or use an online carbon credit exchange to facilitate transactions.
What Are the Challenges of Making Money from Carbon Credits?
While carbon credits offer financial opportunities, there are challenges to consider. Here are the main obstacles:
- Market Volatility: Carbon credit prices can fluctuate significantly due to changes in regulations, supply, and demand.
- Verification Costs: Projects must undergo rigorous verification to ensure they meet standards, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in government policies or carbon pricing mechanisms can impact the profitability of carbon credit projects.
What are the carbon emissions of Nfts?
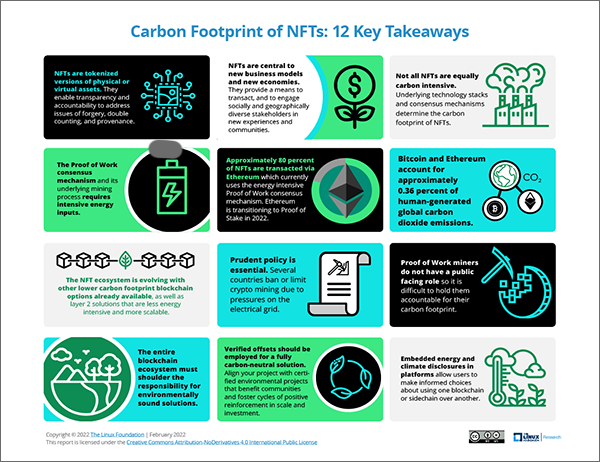
Understanding the Carbon Footprint of NFTs
The carbon emissions of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are primarily linked to the energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms like Ethereum. The process of minting, buying, and selling NFTs involves complex computations that require significant computational power, leading to high energy usage. This energy consumption translates into carbon emissions, especially if the electricity used comes from non-renewable sources.
- Minting NFTs: The creation of an NFT involves solving cryptographic puzzles, which consumes a large amount of energy.
- Transaction Processing: Each transaction on the blockchain, including transfers and sales, requires energy-intensive validation.
- Network Maintenance: The overall maintenance of the blockchain network, including mining and node operations, contributes to carbon emissions.
How Blockchain Technology Impacts Carbon Emissions
Blockchain technology, particularly those using Proof of Work, is inherently energy-intensive. The decentralized nature of blockchain requires multiple nodes to validate transactions, leading to redundant energy consumption. This redundancy ensures security and transparency but at the cost of higher carbon emissions.
- Decentralization: The need for multiple validators increases energy consumption.
- Security Measures: High computational power is required to maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
- Scalability Issues: As the network grows, so does the energy demand, exacerbating carbon emissions.
The Role of Ethereum in NFT Carbon Emissions
Ethereum, the most popular blockchain for NFTs, has been a significant contributor to carbon emissions due to its Proof of Work mechanism. Although Ethereum is transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS) with Ethereum 2.0, the current energy consumption remains high.
- Energy Consumption: Ethereum's PoW mechanism consumes as much energy as some small countries.
- Transition to PoS: Ethereum 2.0 aims to reduce energy consumption by up to 99%, but the transition is ongoing.
- Market Dominance: Ethereum's dominance in the NFT market means its carbon footprint is disproportionately large.
Comparing NFTs to Traditional Art in Terms of Carbon Emissions
While traditional art also has a carbon footprint, primarily from production and transportation, NFTs have a unique and often higher carbon footprint due to their reliance on blockchain technology. The digital nature of NFTs does not eliminate their environmental impact.
- Production: Traditional art involves physical materials, while NFTs involve digital creation and blockchain operations.
- Transportation: NFTs eliminate the need for physical transportation but introduce energy-intensive digital transactions.
- Longevity: The long-term storage and maintenance of NFTs on the blockchain contribute to ongoing energy consumption.
Potential Solutions to Reduce NFT Carbon Emissions
Several solutions are being explored to mitigate the carbon emissions associated with NFTs. These include transitioning to more energy-efficient blockchain technologies, using renewable energy sources, and implementing carbon offset programs.
- Blockchain Upgrades: Transitioning from PoW to PoS can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Renewable Energy: Using renewable energy sources for blockchain operations can lower carbon emissions.
- Carbon Offsetting: NFT platforms can invest in carbon offset programs to neutralize their environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are Carbon Credit NFTs?
Carbon Credit NFTs are a groundbreaking innovation that combines blockchain technology with environmental sustainability. These NFTs represent a digital certificate for a specific amount of carbon credits, which are tradable permits that allow the holder to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. By tokenizing carbon credits into NFTs, they become more transparent, traceable, and easily tradable on digital platforms. This ensures that the credits are not double-counted or fraudulently claimed, providing a more reliable system for carbon offsetting.
How do Carbon Credit NFTs work?
Carbon Credit NFTs operate on blockchain networks, leveraging the technology's inherent features of decentralization and immutability. When a carbon credit is issued, it is converted into an NFT, which is then stored on the blockchain. Each NFT contains metadata that specifies the amount of carbon offset, the project it supports, and its verification details. This allows buyers to verify the authenticity of the carbon credit and track its ownership history. The use of smart contracts automates transactions, ensuring that the credits are transferred securely and efficiently when traded.
Why are Carbon Credit NFTs becoming popular?
The popularity of Carbon Credit NFTs is driven by their ability to address key challenges in the traditional carbon credit market. These include issues like lack of transparency, fraud, and inefficient trading mechanisms. By using blockchain technology, Carbon Credit NFTs provide a verifiable and decentralized solution that appeals to environmentally conscious businesses and individuals. Additionally, the growing interest in sustainable investments and the rise of Web3 technologies have further fueled their adoption, making them a promising tool in the fight against climate change.
What are the benefits of using Carbon Credit NFTs?
Carbon Credit NFTs offer numerous benefits, including enhanced transparency, improved traceability, and greater accessibility. By digitizing carbon credits, they eliminate the risk of double-counting and ensure that each credit is unique and verifiable. This builds trust among buyers and sellers in the carbon market. Furthermore, the use of blockchain technology enables global participation, allowing individuals and organizations from around the world to trade carbon credits seamlessly. This democratization of the carbon market can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy and support global sustainability goals.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles