Australia has committed to achieving net zero emissions by 2050, a target that underscores the nation’s dedication to combating climate change. Among the key sectors driving this transition, sustainable agriculture stands out as a critical player. By adopting innovative practices such as regenerative farming, carbon sequestration, and renewable energy integration, Australian farmers are not only reducing their environmental footprint but also enhancing productivity and resilience. This article explores how sustainable agriculture is spearheading Australia’s journey toward net zero, highlighting the challenges, opportunities, and transformative strategies that are shaping the future of farming in a climate-conscious world.

- Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050: How Sustainable Agriculture Is Leading the Charge
- How is Australia contributing to climate change?
- How is climate change impacting agriculture in Australia?
- How is Climate Change Affecting Crop Yields in Australia?
- What Are the Impacts of Climate Change on Livestock Farming in Australia?
- How is Climate Change Influencing Soil Health in Australian Farmlands?
- What Role Does Climate Change Play in Water Availability for Australian Agriculture?
- How is Climate Change Affecting Pest and Disease Patterns in Australian Agriculture?
- What is net zero by 2050 Australia?
- What is Australia doing for environmental sustainability?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050: How Sustainable Agriculture Is Leading the Charge
Australia has set an ambitious target to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, and sustainable agriculture is playing a pivotal role in this mission. The agricultural sector, which contributes significantly to the country's economy, is also a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. However, through innovative practices and technologies, Australian farmers are transforming the industry into a leader in climate action. This article explores how sustainable agriculture is driving Australia toward its net-zero goal.
The Role of Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable farming practices are at the heart of reducing emissions in agriculture. Techniques such as regenerative farming, precision agriculture, and soil carbon sequestration are being widely adopted. These methods not only reduce emissions but also improve soil health and biodiversity. For instance, regenerative farming focuses on restoring degraded land, which enhances carbon storage in soils. Precision agriculture uses technology to optimize resource use, minimizing waste and emissions.
See Also The Role of CO2 Direct Air Capture in Combating Climate Change: A Path Toward Sustainable Agriculture and Energy
The Role of CO2 Direct Air Capture in Combating Climate Change: A Path Toward Sustainable Agriculture and Energy| Practice | Impact |
|---|---|
| Regenerative Farming | Improves soil health and carbon storage |
| Precision Agriculture | Reduces resource waste and emissions |
| Soil Carbon Sequestration | Captures CO2 from the atmosphere |
Innovative Technologies in Agriculture
The adoption of innovative technologies is revolutionizing Australian agriculture. Tools like drones, sensors, and AI-driven analytics are helping farmers monitor crops, manage water usage, and predict weather patterns more accurately. These technologies enable farmers to make data-driven decisions, reducing their environmental footprint. For example, drones can assess crop health and identify areas needing attention, reducing the need for excessive fertilizer or pesticide use.
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drones | Monitor crop health and reduce chemical use |
| Sensors | Optimize water and resource management |
| AI-Driven Analytics | Enhance decision-making and efficiency |
Government Policies and Incentives
The Australian government is actively supporting the transition to sustainable agriculture through policies and incentives. Programs like the Carbon Farming Initiative and the Emissions Reduction Fund provide financial incentives for farmers to adopt low-emission practices. These initiatives encourage the implementation of projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions or sequester carbon, such as planting trees or improving livestock management.
| Initiative | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Carbon Farming Initiative | Encourages carbon sequestration projects |
| Emissions Reduction Fund | Provides funding for emission reduction projects |
The Impact of Livestock Management
Livestock production is a significant source of emissions in Australia, primarily due to methane from cattle and sheep. However, advancements in livestock management are helping to mitigate these emissions. Strategies such as feed additives, breeding for low-emission animals, and manure management are being implemented. For example, feed additives like seaweed have been shown to reduce methane production in cattle by up to 80%.
See Also Are Carbon Offset Projects Continuously Monitored by Satellite? Are There Insurance Products to Protect These Areas?
Are Carbon Offset Projects Continuously Monitored by Satellite? Are There Insurance Products to Protect These Areas?| Strategy | Effect |
|---|---|
| Feed Additives | Reduce methane emissions from livestock |
| Low-Emission Breeding | Produce animals with lower methane output |
| Manure Management | Minimize emissions from waste |
Collaboration Between Farmers and Researchers
Collaboration between farmers and researchers is crucial for advancing sustainable agriculture. Research institutions are working closely with farmers to develop and test new practices and technologies. This partnership ensures that innovations are practical and effective in real-world farming conditions. For instance, research on cover cropping and rotational grazing has provided farmers with actionable insights to improve sustainability.
| Collaboration | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Cover Cropping Research | Improves soil health and reduces erosion |
| Rotational Grazing Studies | Enhances pasture productivity and carbon storage |
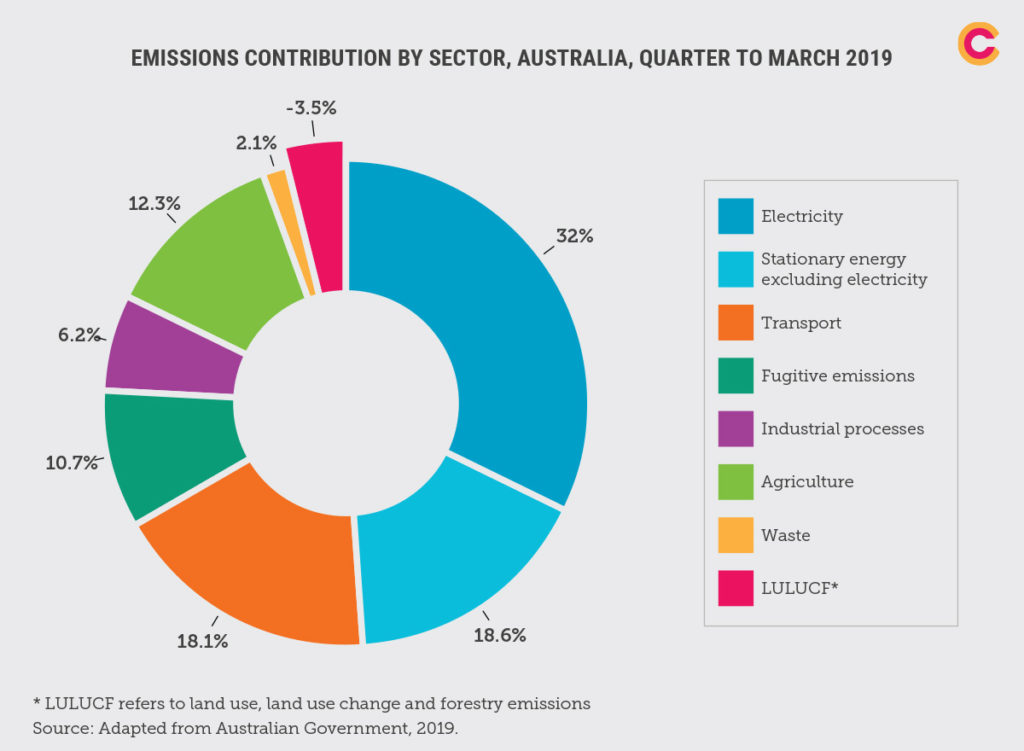
How is Australia contributing to climate change?
Australia's Reliance on Fossil Fuels
Australia is one of the world's largest exporters of coal and natural gas, which significantly contributes to global greenhouse gas emissions. The country's economy heavily relies on fossil fuel extraction and export, making it a key player in climate change. Key points include:
See Also How Common Are Carbon Offsetting Programs in Large Businesses?
How Common Are Carbon Offsetting Programs in Large Businesses?- Australia is the second-largest exporter of coal globally, supplying energy to countries like China and India.
- The extraction and burning of fossil fuels release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
- Domestic energy production in Australia still depends heavily on coal-fired power plants.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
Australia's land use practices, including deforestation and land clearing, contribute significantly to climate change. These activities reduce the number of trees that can absorb CO2, exacerbating the problem. Key points include:
- Large-scale land clearing for agriculture, particularly in Queensland, releases stored carbon into the atmosphere.
- Deforestation reduces biodiversity and disrupts ecosystems that act as carbon sinks.
- Land use changes contribute to soil degradation, further increasing greenhouse gas emissions.
High Per Capita Emissions
Australia has one of the highest per capita greenhouse gas emissions in the world, driven by its energy-intensive lifestyle and industrial activities. Key points include:
- Australians consume large amounts of energy for transportation, heating, and cooling due to the country's vast distances and extreme weather conditions.
- The reliance on private vehicles over public transportation increases emissions from the transport sector.
- Industrial activities, such as mining and manufacturing, are energy-intensive and contribute significantly to emissions.
Limited Renewable Energy Adoption
Despite having abundant natural resources for renewable energy, Australia has been slow to transition away from fossil fuels. Key points include:
- While solar and wind energy potential is high, the share of renewables in the energy mix remains relatively low compared to fossil fuels.
- Government policies have historically favored fossil fuel industries over renewable energy investments.
- Inconsistent renewable energy policies have hindered large-scale adoption and innovation in the sector.
Export of Emissions Through Resources
Australia's role as a major exporter of fossil fuels means it indirectly contributes to emissions in other countries. Key points include:
- Exported coal and gas are burned in other nations, adding to global greenhouse gas emissions.
- The country's economic reliance on fossil fuel exports creates a conflict between economic growth and climate action.
- Australia's exported emissions are not accounted for in its domestic carbon accounting, masking its true contribution to climate change.
How is climate change impacting agriculture in Australia?
How is Climate Change Affecting Crop Yields in Australia?
Climate change is significantly impacting crop yields in Australia due to rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events. These factors are disrupting traditional farming practices and reducing productivity.
- Heat stress on crops like wheat and barley reduces their growth and yield.
- Droughts are becoming more frequent, leading to water shortages for irrigation.
- Flooding caused by intense rainfall events damages crops and soil structure.
What Are the Impacts of Climate Change on Livestock Farming in Australia?
Livestock farming in Australia is facing challenges due to heat stress, water scarcity, and reduced feed availability, all exacerbated by climate change.
- Heat stress affects animal health, reducing milk production and fertility rates.
- Water scarcity forces farmers to rely on expensive alternatives for livestock hydration.
- Reduced pasture quality due to droughts limits feed availability, increasing costs for supplementary feed.
How is Climate Change Influencing Soil Health in Australian Farmlands?
Climate change is degrading soil health in Australia through erosion, salinization, and loss of organic matter, which are critical for sustainable agriculture.
- Erosion caused by heavy rainfall and wind strips away fertile topsoil.
- Salinization increases due to rising sea levels and reduced rainfall, affecting soil fertility.
- Loss of organic matter occurs as higher temperatures accelerate decomposition rates.
What Role Does Climate Change Play in Water Availability for Australian Agriculture?
Climate change is altering water availability in Australia, with droughts, reduced river flows, and depleted groundwater becoming more common.
- Droughts reduce surface water availability, impacting irrigation systems.
- Reduced river flows affect water allocations for farming communities.
- Depleted groundwater resources limit long-term water security for agriculture.
How is Climate Change Affecting Pest and Disease Patterns in Australian Agriculture?
Climate change is altering pest and disease dynamics in Australian agriculture, with warmer temperatures and changing rainfall patterns creating favorable conditions for outbreaks.
- Warmer temperatures allow pests like locusts and fruit flies to thrive and expand their range.
- Increased humidity from erratic rainfall promotes fungal diseases in crops.
- New invasive species are emerging as climate conditions shift, threatening native crops and livestock.
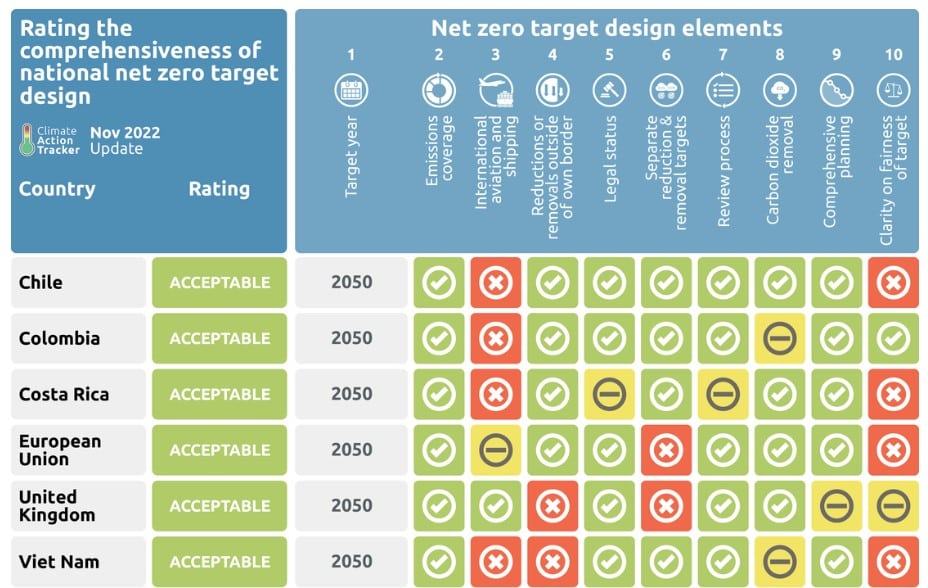
What is net zero by 2050 Australia?
![]()
What Does Net Zero by 2050 Mean for Australia?
Net zero by 2050 refers to Australia's commitment to balancing the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere with the amount removed. This means that by 2050, Australia aims to achieve a state where its carbon emissions are offset by carbon removal efforts, such as reforestation or carbon capture technologies. The goal is to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
- Carbon neutrality: Achieving a balance between emissions produced and emissions removed.
- Renewable energy: Transitioning to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Policy frameworks: Implementing government policies and regulations to support the transition to net zero.
Why is Net Zero by 2050 Important for Australia?
Net zero by 2050 is crucial for Australia to mitigate the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss. As one of the world's largest per capita emitters of greenhouse gases, Australia has a significant role to play in global climate action. Achieving net zero will also position Australia as a leader in the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Environmental protection: Reducing emissions to preserve ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Economic opportunities: Creating jobs and industries in renewable energy and green technologies.
- Global responsibility: Contributing to international efforts to combat climate change.
How Will Australia Achieve Net Zero by 2050?
Australia plans to achieve net zero by 2050 through a combination of technological innovation, policy measures, and behavioral changes. Key strategies include increasing the share of renewable energy in the energy mix, improving energy efficiency, and investing in carbon capture and storage technologies. The government is also working with businesses and communities to ensure a just and equitable transition.
- Renewable energy expansion: Scaling up solar, wind, and hydroelectric power generation.
- Energy efficiency: Implementing measures to reduce energy consumption in industries and households.
- Carbon capture: Developing technologies to capture and store carbon emissions from industrial processes.
What Are the Challenges for Australia in Achieving Net Zero by 2050?
Australia faces several challenges in achieving net zero by 2050, including its reliance on coal and gas exports, political resistance to climate policies, and the need for significant investment in new technologies. Additionally, transitioning to a low-carbon economy requires addressing social and economic impacts, such as job losses in traditional industries and ensuring energy affordability for all Australians.
- Economic dependence: Reducing reliance on fossil fuel exports while diversifying the economy.
- Political hurdles: Navigating differing views on climate policy across political parties.
- Social equity: Ensuring a fair transition for workers and communities affected by the shift to renewable energy.
What Role Do Businesses and Individuals Play in Achieving Net Zero by 2050?
Businesses and individuals have a critical role in helping Australia achieve net zero by 2050. Companies can adopt sustainable practices, invest in renewable energy, and reduce their carbon footprints. Individuals can contribute by making energy-efficient choices, supporting renewable energy initiatives, and advocating for stronger climate policies. Collective action is essential to drive the systemic changes needed to reach net zero.
- Corporate responsibility: Businesses adopting green practices and reducing emissions.
- Consumer choices: Individuals opting for sustainable products and energy sources.
- Advocacy: Supporting policies and initiatives that promote climate action.
What is Australia doing for environmental sustainability?
Renewable Energy Initiatives
Australia is actively investing in renewable energy to reduce its carbon footprint and transition away from fossil fuels. Key initiatives include:
- Expanding solar energy projects, including large-scale solar farms and rooftop solar installations.
- Developing wind energy infrastructure, particularly in regions with high wind potential.
- Investing in battery storage systems to stabilize the grid and store excess renewable energy.
Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Australia is working to preserve its unique biodiversity and ecosystems through various conservation programs. Key efforts include:
- Establishing and managing national parks and marine protected areas.
- Implementing programs to combat invasive species that threaten native wildlife.
- Restoring degraded habitats, such as wetlands and forests, to support endangered species.
Waste Management and Recycling
Australia is addressing waste management challenges by promoting recycling and reducing landfill waste. Key strategies include:
- Implementing single-use plastic bans to reduce plastic pollution.
- Encouraging circular economy practices to reuse and recycle materials.
- Investing in waste-to-energy technologies to convert waste into usable energy.
Climate Change Mitigation Policies
Australia is committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions through climate change mitigation policies. Key measures include:
- Setting emissions reduction targets under international agreements like the Paris Accord.
- Promoting carbon farming to sequester carbon in agricultural lands.
- Supporting clean energy innovation through research and development funding.
Sustainable Water Management
Australia is focusing on sustainable water management to address water scarcity and ensure long-term availability. Key initiatives include:
- Implementing water recycling programs to reuse treated wastewater.
- Investing in desalination plants to provide fresh water in drought-prone areas.
- Promoting water-efficient practices in agriculture and urban areas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050?
Australia's Net Zero Goal by 2050 is a commitment to achieve a balance between the amount of greenhouse gases emitted and the amount removed from the atmosphere. This means that by 2050, Australia aims to reduce its carbon emissions to as close to zero as possible and offset any remaining emissions through methods like carbon sequestration and renewable energy projects. The goal is part of a global effort to combat climate change and limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
How is sustainable agriculture contributing to Australia's Net Zero Goal?
Sustainable agriculture plays a critical role in helping Australia achieve its Net Zero Goal by 2050. Practices such as regenerative farming, soil carbon sequestration, and reduced use of synthetic fertilizers are being adopted to lower emissions from the agricultural sector. Additionally, sustainable agriculture promotes biodiversity, improves soil health, and enhances water efficiency, all of which contribute to reducing the sector's carbon footprint. By integrating these practices, Australia is not only reducing emissions but also building resilience against the impacts of climate change.
What are the challenges Australia faces in achieving Net Zero by 2050?
Australia faces several challenges in reaching its Net Zero Goal by 2050. These include transitioning away from fossil fuels, which currently dominate the country's energy mix, and addressing emissions from sectors like transport and heavy industry. Additionally, the agricultural sector must balance productivity with sustainability, which can be complex due to varying climates and land use. Financial investments, technological advancements, and policy support are essential to overcome these challenges and ensure a smooth transition to a low-carbon economy.
What role do farmers play in Australia's sustainable agriculture efforts?
Farmers are at the forefront of Australia's sustainable agriculture efforts. They are adopting innovative practices such as precision farming, agroforestry, and rotational grazing to reduce emissions and improve land management. Many farmers are also participating in carbon credit programs, which reward them for implementing practices that sequester carbon in the soil. By embracing these methods, farmers are not only contributing to Australia's Net Zero Goal but also ensuring the long-term viability of their land and livelihoods.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles